Back
Present
Facts for Kids
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, energy, and the relationships between them in various processes.

Explore the internet with AstroSafe
Search safely, manage screen time, and remove ads and inappropriate content with the AstroSafe Browser.
Download
Inside this Article
Second Law Of Thermodynamics
Laws Of Thermodynamics
Temperature
Ice Cream
Boiling
Weather
Energy
Kelvin
State
Did you know?
🌡️ Thermodynamics is the study of heat and temperature and their relation to energy and work.
🔄 The first law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed.
❄️ The second law of thermodynamics addresses the direction of energy transfer, stating that heat will naturally flow from hot to cold.
⚙️ A thermodynamic system can be open, closed, or isolated based on its interaction with its surroundings.
🔥 The concept of entropy is crucial in thermodynamics, representing the degree of disorder or randomness in a system.
🔋 Heat engines are devices that convert thermal energy into mechanical work, optimized by Carnot efficiency.
🌀 The ideal gas law is a fundamental equation in thermodynamics that relates pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles.
🔬 Thermodynamics is foundational in chemistry, particularly in predicting reaction spontaneity and equilibrium.
🏭 The Rankine cycle and the refrigeration cycle are processes used in power generation and cooling, respectively.
🌌 Thermodynamic principles apply not just to engines, but also to biological systems and even the universe itself.
Show Less

Become a Creator with DIY.org
A safe online space featuring over 5,000 challenges to create, explore and learn in.
Learn more
Overview
Thermodynamics is the study of heat, energy, and how things move! 🔥✅ It helps us understand how engines work, what makes ice melt, and even why ice cream is cold! 🍦💨 Thermodynamics has four main laws that tell us how energy behaves in different situations. The word comes from "thermo," meaning heat, and "dynamics," which means movement. Every time you see a car driving or a kettle boiling, you're observing thermodynamics in action! 🚗💧 It's all around us, making it an important part of science and daily life!
Read Less
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is how heat energy moves from one place to another! 🔥
There are three types of heat transfer:
1. Conduction: This happens when heat moves through touching. Like when a metal spoon gets hot in a pot! 🍴🔥
2. Convection: This is when fluids, like air or water, move and carry heat with them. Think of warm air rising in a hot air balloon! 🎈💨
3. Radiation: This is heat transfer through empty space, like the warmth you feel from the Sun! ☀
️❤️
Understanding heat transfer is important for cooking, comfort, and many technologies!
There are three types of heat transfer:
1. Conduction: This happens when heat moves through touching. Like when a metal spoon gets hot in a pot! 🍴🔥
2. Convection: This is when fluids, like air or water, move and carry heat with them. Think of warm air rising in a hot air balloon! 🎈💨
3. Radiation: This is heat transfer through empty space, like the warmth you feel from the Sun! ☀
️❤️
Understanding heat transfer is important for cooking, comfort, and many technologies!
Read Less
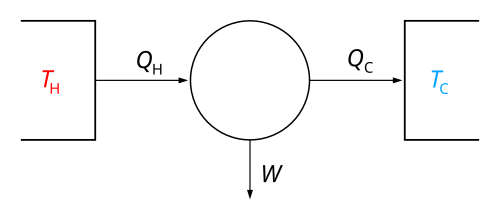
Thermodynamic Cycles
A thermodynamic cycle is a series of changes that a system goes through, returning to its original state. 🔄
One famous example is the Carnot Cycle, used in heat engines! 🚂
The cycle has four main steps:
1. Heating: Adding heat to the engine. 🔥
2. Work Done: The engine does work by moving. 🏋
️
3. Cooling: Heat leaves the engine. ❄
️
4. Rest: The engine returns to its starting state. 🛑
These cycles are important for making efficient engines and refrigerators, helping us harness energy better!
One famous example is the Carnot Cycle, used in heat engines! 🚂
The cycle has four main steps:
1. Heating: Adding heat to the engine. 🔥
2. Work Done: The engine does work by moving. 🏋
️
3. Cooling: Heat leaves the engine. ❄
️
4. Rest: The engine returns to its starting state. 🛑
These cycles are important for making efficient engines and refrigerators, helping us harness energy better!
Read Less
Thermodynamic Systems
A thermodynamic system is a group of objects we study to see how heat and energy change. 🌍
There are three main types of systems:
1. Open Systems: These can exchange energy and matter with their environment, like a boiling pot! 🍲
2. Closed Systems: They exchange energy but not matter, like a sealed bottle of soda. 🥤
3. Isolated Systems: They don’t exchange anything with their surroundings, similar to a thermos bottle! 🧊🚫
Studying these systems helps scientists learn how energy travels and transforms in many everyday situations!
There are three main types of systems:
1. Open Systems: These can exchange energy and matter with their environment, like a boiling pot! 🍲
2. Closed Systems: They exchange energy but not matter, like a sealed bottle of soda. 🥤
3. Isolated Systems: They don’t exchange anything with their surroundings, similar to a thermos bottle! 🧊🚫
Studying these systems helps scientists learn how energy travels and transforms in many everyday situations!
Read Less
Historical Development
The study of thermodynamics began in the 19th century! 📜🔍 Scientists wanted to understand how engines worked. In 1824, Sadi Carnot explained how heat engines operated, laying the groundwork for thermodynamics! 🚂💡 A few decades later, James Clerk Maxwell and Ludwig Boltzmann helped develop concepts like statistical mechanics, explaining why things behave the way they do. 🌌
This led to the establishment of the laws of thermodynamics, which are still used today! 🏆
Thermodynamics has improved our lives and technology in numerous ways!
This led to the establishment of the laws of thermodynamics, which are still used today! 🏆
Thermodynamics has improved our lives and technology in numerous ways!
Read Less
Laws of Thermodynamics
There are four main laws of thermodynamics:
1. Zeroth Law: If two things are the same temperature, they are in thermal equilibrium. 🌡
️
2. First Law: Energy can't be created or destroyed; it only changes forms—for example, from fuel to motion. 🔄
3. Second Law: Heat flows naturally from hot to cold areas, like ice melting in the sun! ☀
️❄️
4. Third Law: As things cool down, they get closer to absolute zero, the coldest temperature possible at -273°C! ❄
️🧊
These laws guide scientists and engineers in understanding how energy works!
1. Zeroth Law: If two things are the same temperature, they are in thermal equilibrium. 🌡
️
2. First Law: Energy can't be created or destroyed; it only changes forms—for example, from fuel to motion. 🔄
3. Second Law: Heat flows naturally from hot to cold areas, like ice melting in the sun! ☀
️❄️
4. Third Law: As things cool down, they get closer to absolute zero, the coldest temperature possible at -273°C! ❄
️🧊
These laws guide scientists and engineers in understanding how energy works!
Read Less
Entropy and Its Significance
Entropy is a measure of disorder or randomness. Imagine your messy room! 🛏
️ When energy spreads out or becomes less organized, entropy increases. 🌪
️ The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the total entropy of a closed system always increases over time, which means things tend to get messier! This helps explain why ice melts and why our rooms get cluttered! 🥴
Keeping things tidy requires energy to fight against the ever-increasing entropy. So remember, entropy is about how energy and order change!
️ When energy spreads out or becomes less organized, entropy increases. 🌪
️ The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that the total entropy of a closed system always increases over time, which means things tend to get messier! This helps explain why ice melts and why our rooms get cluttered! 🥴
Keeping things tidy requires energy to fight against the ever-increasing entropy. So remember, entropy is about how energy and order change!
Read Less
Key Figures in Thermodynamics
Several important scientists made big contributions to thermodynamics! 🌟
1. Sadi Carnot: Known as the "father of thermodynamics," he studied heat engines. 🚂
2. James Prescott Joule: Discovered the relationship between heat and energy. 🔋
3. Ludwig Boltzmann: Developed ideas about the behavior of particles and heat. ⚛
️
4. William Thomson (Lord Kelvin): Helped create the Kelvin temperature scale! 🌡
️
These pioneers helped us understand heat, energy, and how they affect our world! Their work continues to inspire scientists today! 📚💖
1. Sadi Carnot: Known as the "father of thermodynamics," he studied heat engines. 🚂
2. James Prescott Joule: Discovered the relationship between heat and energy. 🔋
3. Ludwig Boltzmann: Developed ideas about the behavior of particles and heat. ⚛
️
4. William Thomson (Lord Kelvin): Helped create the Kelvin temperature scale! 🌡
️
These pioneers helped us understand heat, energy, and how they affect our world! Their work continues to inspire scientists today! 📚💖
Read Less
Applications of Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is used in many exciting ways! 🔬🚀 It helps design engines for cars and rockets, ensuring they run efficiently! 🚗💨 Scientists use thermodynamics to understand weather patterns and improve air conditioning and heating systems for comfort at home. 🌈🏡 It also plays a key role in making food safe to eat through cooking methods! 🍳✅ There are even applications in renewable energy, helping create better solar panels! 🌱☀️ Overall, thermodynamics helps us solve real-world problems and invent new technologies!
Read Less
Try your luck with the Thermodynamics Quiz.
Try this Thermodynamics quiz and see how many you score!
Q1
Question 1 of 10
Next
Explore More