Present
Facts for Kids
Subatomic particles are tiny bits that make up atoms, which are the building blocks of everything around us.

Explore the internet with AstroSafe
Search safely, manage screen time, and remove ads and inappropriate content with the AstroSafe Browser.
Download
Inside this Article
Strong Nuclear Force
Ernest Rutherford
Quantum Mechanics
Particle Physics
Switzerland
Atomic Mass
Dark Matter
Universe
Energy
Are
Did you know?
🔬 Everything around you is made of tiny particles called atoms, and even atoms are made of smaller bits called subatomic particles!
🌀 The three main types of subatomic particles are protons, neutrons, and electrons.
🌌 Protons are positively charged, neutrons have no charge, and electrons are negatively charged.
⚡ Protons and neutrons are much heavier than electrons.
🌈 Electrons zoom around the nucleus of an atom in paths called orbits.
💡 J.J. Thomson discovered the electron in the late 1800s!
🏆 Ernest Rutherford discovered protons by studying how particles passed through gold foil in 1911.
🧬 James Chadwick discovered neutrons in 1932, completing the picture of the atom.
⚗️ The arrangement of particles in an atom determines what type of atom it is.
🚀 Particle accelerators speed up particles to help scientists study them better.
Show Less

Become a Creator with DIY.org
A safe online space featuring over 5,000 challenges to create, explore and learn in.
Learn more
Overview
Did you know that everything around you is made up of tiny particles? 🧊
An atom is the smallest unit of matter, but even atoms are made of smaller bits called subatomic particles! These include protons, neutrons, and electrons. Atoms are so small that you can't see them with your eyes! They make up everything from trees 🌳 to the air you breathe 🍃. Exploring subatomic particles helps scientists understand how matter behaves. It’s like discovering building blocks to the universe! These little guys also help in making cool technologies like smartphones. Isn’t science amazing? 🌟
An atom is the smallest unit of matter, but even atoms are made of smaller bits called subatomic particles! These include protons, neutrons, and electrons. Atoms are so small that you can't see them with your eyes! They make up everything from trees 🌳 to the air you breathe 🍃. Exploring subatomic particles helps scientists understand how matter behaves. It’s like discovering building blocks to the universe! These little guys also help in making cool technologies like smartphones. Isn’t science amazing? 🌟
Read Less
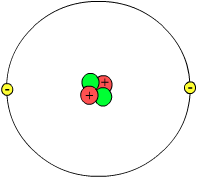
Structure of an Atom
An atom is like a tiny solar system! 🌌
At the center, there’s the nucleus made up of protons and neutrons. Imagine the nucleus as the sun, and then picture electrons zooming around it like planets!
The electrons travel in paths called energy levels or shells. Each shell can hold a certain number of electrons. The first shell holds 2, the second holds 8, and the third can hold 18! 🌍
The way these particles are arranged helps determine what kind of atom it is. For example, a carbon atom has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons. That’s what makes it a carbon atom!
At the center, there’s the nucleus made up of protons and neutrons. Imagine the nucleus as the sun, and then picture electrons zooming around it like planets!
The electrons travel in paths called energy levels or shells. Each shell can hold a certain number of electrons. The first shell holds 2, the second holds 8, and the third can hold 18! 🌍
The way these particles are arranged helps determine what kind of atom it is. For example, a carbon atom has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons. That’s what makes it a carbon atom!
Read Less
Particle Accelerators
Particle accelerators are huge machines that speed up particles to near-light speeds! 🚀
These machines help scientists study subatomic particles by smashing them together, allowing researchers to observe what happens.
One famous particle accelerator is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Switzerland. It can accelerate protons and collide them at incredible speeds, helping discover particles like the Higgs boson! 🔬
These machines are essential for exploring the tiniest building blocks of the universe and finding out how they interact. They're like giant playgrounds for scientists! 🎢
These machines help scientists study subatomic particles by smashing them together, allowing researchers to observe what happens.
One famous particle accelerator is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Switzerland. It can accelerate protons and collide them at incredible speeds, helping discover particles like the Higgs boson! 🔬
These machines are essential for exploring the tiniest building blocks of the universe and finding out how they interact. They're like giant playgrounds for scientists! 🎢
Read Less
Historical Discoveries
The journey of discovering subatomic particles started with some amazing scientists! 💡
In the late 1800s, J.J. Thomson found the electron. He blew everyone's minds by saying atoms aren’t indivisible! Then, in 1911, Ernest Rutherford discovered protons by studying how particles passed through gold foil.
Later, in 1932, James Chadwick discovered neutrons, which helped complete the picture of the atom! 🏆
These discoveries led to what we know about atoms today. So, when you think of atoms, remember the incredible scientists who explored the tiniest bits of matter!
In the late 1800s, J.J. Thomson found the electron. He blew everyone's minds by saying atoms aren’t indivisible! Then, in 1911, Ernest Rutherford discovered protons by studying how particles passed through gold foil.
Later, in 1932, James Chadwick discovered neutrons, which helped complete the picture of the atom! 🏆
These discoveries led to what we know about atoms today. So, when you think of atoms, remember the incredible scientists who explored the tiniest bits of matter!
Read Less
Interactions and Forces
Subatomic particles interact with each other through forces! ⚔
️ The electromagnetic force pulls oppositely charged particles together. So, protons and electrons attract each other, which keeps the atom stable!
Another important force is the strong nuclear force, which holds protons and neutrons tightly in the nucleus, keeping it from flying apart. These forces are super strong but only act over very short distances! 🏋
️♂️ The weak nuclear force is involved in processes like radioactive decay. Understanding these forces helps scientists grasp how matter works and interacts in the universe! 🌌
️ The electromagnetic force pulls oppositely charged particles together. So, protons and electrons attract each other, which keeps the atom stable!
Another important force is the strong nuclear force, which holds protons and neutrons tightly in the nucleus, keeping it from flying apart. These forces are super strong but only act over very short distances! 🏋
️♂️ The weak nuclear force is involved in processes like radioactive decay. Understanding these forces helps scientists grasp how matter works and interacts in the universe! 🌌
Read Less
Role in Quantum Mechanics
Quantum mechanics is a fascinating area of physics that studies the behavior of subatomic particles! ✨
At this tiny level, things get really strange. For example, particles can exist in multiple places at once! This is called "superposition."
When scientists try to observe them, they behave like they 'know' they are being watched. This is due to "wave-particle duality," where particles show both wave-like and particle-like properties. 🎢
Understanding quantum mechanics helps scientists develop new technologies, like lasers and computers. It’s like a magic show happening at the smallest levels of our world! 🎩
At this tiny level, things get really strange. For example, particles can exist in multiple places at once! This is called "superposition."
When scientists try to observe them, they behave like they 'know' they are being watched. This is due to "wave-particle duality," where particles show both wave-like and particle-like properties. 🎢
Understanding quantum mechanics helps scientists develop new technologies, like lasers and computers. It’s like a magic show happening at the smallest levels of our world! 🎩
Read Less
Applications in Technology
Subatomic particles play a vital role in many everyday technologies! 📱
For example, semiconductors in electronics, made of silicon atoms, allow electricity to flow when certain conditions are met, thanks to the behavior of electrons!
Particle physics also leads to medical advancements! PET scans use positrons (anti-electrons) to create detailed images of the body. 🌡
️ And don't forget about MRI machines! They use the properties of protons to create images of our insides. From cellphones to medical tools, subatomic particle science helps shape our modern world!
For example, semiconductors in electronics, made of silicon atoms, allow electricity to flow when certain conditions are met, thanks to the behavior of electrons!
Particle physics also leads to medical advancements! PET scans use positrons (anti-electrons) to create detailed images of the body. 🌡
️ And don't forget about MRI machines! They use the properties of protons to create images of our insides. From cellphones to medical tools, subatomic particle science helps shape our modern world!
Read Less
Types of Subatomic Particles
There are three main types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons! 🌀
Protons are positively charged and found in the center of an atom, called the nucleus. Neutrons are neutral, meaning they have no charge and are also found in the nucleus. 🔴
Electrons are negatively charged particles that zoom around the nucleus in paths called orbits.
Protons and neutrons are much heavier than electrons, with protons weighing about 1 atomic mass unit (amu) and neutrons weighing about 1 amu too! But electrons are super light, around 1/1836 of an amu! Isn’t it fascinating how these tiny pieces create everything around us? 🌈
Protons are positively charged and found in the center of an atom, called the nucleus. Neutrons are neutral, meaning they have no charge and are also found in the nucleus. 🔴
Electrons are negatively charged particles that zoom around the nucleus in paths called orbits.
Protons and neutrons are much heavier than electrons, with protons weighing about 1 atomic mass unit (amu) and neutrons weighing about 1 amu too! But electrons are super light, around 1/1836 of an amu! Isn’t it fascinating how these tiny pieces create everything around us? 🌈
Read Less
Current Research and Discoveries
Scientists are continually researching subatomic particles to uncover new discoveries! 🧬
For instance, researchers are exploring dark matter, an invisible substance that makes up most of the universe but doesn’t interact with light.
They are also studying neutrinos, very light particles that can pass through matter easily, to learn more about the universe's creation! 🌌
Projects like the Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment in the USA focus on these tiny particles. Each new finding helps us better understand how our universe works, revealing the mysteries hidden in the smallest building blocks of matter! 🌟
For instance, researchers are exploring dark matter, an invisible substance that makes up most of the universe but doesn’t interact with light.
They are also studying neutrinos, very light particles that can pass through matter easily, to learn more about the universe's creation! 🌌
Projects like the Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment in the USA focus on these tiny particles. Each new finding helps us better understand how our universe works, revealing the mysteries hidden in the smallest building blocks of matter! 🌟
Read Less
Properties of Subatomic Particles
Subatomic particles have unique properties that make them special! ⚡
Protons, neutrons, and electrons differ in charge: protons are positive (+1), electrons are negative (-1), and neutrons are neutral (0).
Their mass also varies. Protons and neutrons are heavier compared to electrons. Protons hold a significant part of an atom's weight, while electrons are lightweights and barely add to it. This balance forms the identity of different elements on the periodic table! ⚗
️ Understanding these properties helps scientists predict how atoms will interact in different situations, like chemical reactions!
Protons, neutrons, and electrons differ in charge: protons are positive (+1), electrons are negative (-1), and neutrons are neutral (0).
Their mass also varies. Protons and neutrons are heavier compared to electrons. Protons hold a significant part of an atom's weight, while electrons are lightweights and barely add to it. This balance forms the identity of different elements on the periodic table! ⚗
️ Understanding these properties helps scientists predict how atoms will interact in different situations, like chemical reactions!
Read Less
Try your luck with the Subatomic Particle Quiz.
Try this Subatomic Particle quiz and see how many you score!
Q1
Question 1 of 10
Next
Explore More