Present
Facts for Kids
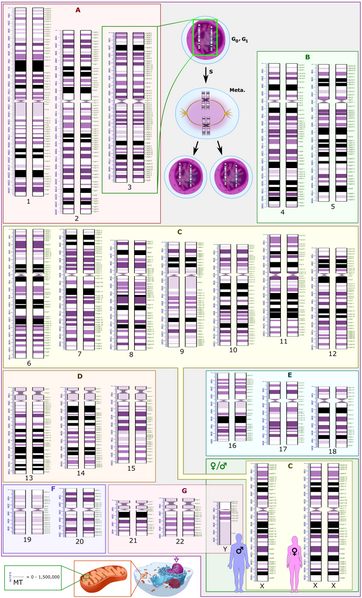
The human genome is the complete set of DNA instructions that guide the building and functioning of a human being, containing about 20,000 to 25,000 genes across 23 chromosome pairs.

Explore the internet with AstroSafe
Search safely, manage screen time, and remove ads and inappropriate content with the AstroSafe Browser.
Download
Inside this Article
Gene Therapy
Information
Function
Cytosine
Genetics
Medicine
Genomics
Embryo
Genome
People
Did you know?
📚 The human genome is like a giant instruction manual for our bodies!
🌍 Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes that hold our DNA.
❤️ The genome is made of DNA, which carries important instructions for living things.
🦶 Each person's genome is unique, just like a fingerprint.
🌞 If you stretched out all your DNA, it could reach to the Sun and back over 300 times!
🌀 DNA looks like a twisted ladder, and scientists call it a double helix.
🌱 Genes are tiny instructions that tell our bodies how to grow and function.
🕒 The Human Genome Project mapped out all the genes in the human genome between 1990 and 2003.
🌈 Genetic variation makes each person special with small differences in their DNA.
💉 Genomic research can lead to personalized medicine, treating people based on their DNA.
Show Less

Become a Creator with DIY.org
A safe online space featuring over 5,000 challenges to create, explore and learn in.
Learn more
Overview
The human genome is like a giant instruction manual for our bodies! 📚
It is made up of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which is found in all our cells. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, which are long strands of DNA. These chromosomes are located in the nucleus, the control center of each cell. The human genome has about 3 billion base pairs—like a super long word! 🌍
Scientists study the genome to understand how traits like eye color or height are passed down from parents to kids. It helps us learn about health, diseases, and how our bodies work!
It is made up of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), which is found in all our cells. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, which are long strands of DNA. These chromosomes are located in the nucleus, the control center of each cell. The human genome has about 3 billion base pairs—like a super long word! 🌍
Scientists study the genome to understand how traits like eye color or height are passed down from parents to kids. It helps us learn about health, diseases, and how our bodies work!
Read Less
Structure of DNA
DNA looks like a twisted ladder, and scientists call it a double helix! 🌀
The rungs of the ladder are made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up: A with T and C with G. This pairing forms the steps of the ladder. The sides of the ladder are made of sugar and phosphate molecules. Together, these structures help protect our DNA! 💪
Each person has a slightly different DNA sequence, making us unique! It also allows us to pass on traits and characteristics to our children.
The rungs of the ladder are made up of four chemical bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up: A with T and C with G. This pairing forms the steps of the ladder. The sides of the ladder are made of sugar and phosphate molecules. Together, these structures help protect our DNA! 💪
Each person has a slightly different DNA sequence, making us unique! It also allows us to pass on traits and characteristics to our children.
Read Less
Comparative Genomics
Comparative genomics is the study of the DNA of different species! 🦁🔬 Scientists look at similarities and differences between the genomes of humans, mice, and even fruit flies! This helps us understand evolution, which is how living things change over time. By comparing genomes, scientists can spot important genes that are shared among species. For example, humans and chimpanzees share about 98% of their DNA! 🐒
Learning from comparative genomics helps scientists uncover clues about diseases and how organisms adapt to their environments.
Learning from comparative genomics helps scientists uncover clues about diseases and how organisms adapt to their environments.
Read Less
The Human Genome Project
The Human Genome Project was a huge science project that started in 1990 and finished in 2003! 🕒
It aimed to map out all the genes in the human genome. International scientists worked together to read the DNA of humans and identify about 20,000 genes. 🌐
This project took 13 years, and it helped us discover many important things about genetics. It cost about $3 billion, but now we have better tools to fight diseases. Thanks to this project, research in genetics has advanced immensely, making life better for many people!
It aimed to map out all the genes in the human genome. International scientists worked together to read the DNA of humans and identify about 20,000 genes. 🌐
This project took 13 years, and it helped us discover many important things about genetics. It cost about $3 billion, but now we have better tools to fight diseases. Thanks to this project, research in genetics has advanced immensely, making life better for many people!
Read Less
What is the Human Genome?
The human genome contains all the genetic information necessary for building and maintaining a person. ❤
️ It is composed of DNA, which carries the instructions for living things. In humans, our genome has about 20,000 to 25,000 genes, which are specific segments of DNA that help determine traits. Our genome is unique, like a fingerprint! 🦶
For fun, did you know that if you stretched out all the DNA in your body, it could reach to the Sun and back over 300 times? 🌞
Isn’t that amazing?
️ It is composed of DNA, which carries the instructions for living things. In humans, our genome has about 20,000 to 25,000 genes, which are specific segments of DNA that help determine traits. Our genome is unique, like a fingerprint! 🦶
For fun, did you know that if you stretched out all the DNA in your body, it could reach to the Sun and back over 300 times? 🌞
Isn’t that amazing?
Read Less
Future of Genomic Medicine
The future of genomic medicine looks bright! 🌟
As scientists continue to unlock the secrets of the genome, they aim to create more personalized treatments for diseases. Imagine a doctor being able to look at your DNA to find the best medicine just for you! 💊
Additionally, researchers hope to use genomic data to discover new therapies for challenging conditions like cancer or genetic disorders. There are also exciting possibilities in gene therapy, which could lead to curing genetic diseases. The advancements in genomics will help improve everyone’s health! 🏥
As scientists continue to unlock the secrets of the genome, they aim to create more personalized treatments for diseases. Imagine a doctor being able to look at your DNA to find the best medicine just for you! 💊
Additionally, researchers hope to use genomic data to discover new therapies for challenging conditions like cancer or genetic disorders. There are also exciting possibilities in gene therapy, which could lead to curing genetic diseases. The advancements in genomics will help improve everyone’s health! 🏥
Read Less
Key Genes and Their Functions
Genes are like tiny instructions that tell our bodies how to grow and function! 🌱
For example, the gene called “OCA2” influences our eye color. If a child has a version of this gene, they might have blue eyes! Another important gene is “TP53,” which helps protect our bodies from cancer. 🦠
Genes can also help determine if we are tall or short! With about 20,000 genes, there are many combinations that make us all special. Learning about these genes helps scientists understand diseases and our health better!
For example, the gene called “OCA2” influences our eye color. If a child has a version of this gene, they might have blue eyes! Another important gene is “TP53,” which helps protect our bodies from cancer. 🦠
Genes can also help determine if we are tall or short! With about 20,000 genes, there are many combinations that make us all special. Learning about these genes helps scientists understand diseases and our health better!
Read Less
Applications of Genomic Research
Genomic research helps scientists make amazing discoveries! 🧬
It has many applications in medicine and health. For example, researchers can use our genome to find out if a person is at risk for certain diseases and suggest ways to prevent them. They can also develop personalized medicine, which means someone can get specific treatments based on their DNA! 💉
Moreover, genomic research is used in agriculture, helping scientists create plants that grow better or resist diseases! 🌱
Overall, this research opens up new possibilities for improving our lives.
It has many applications in medicine and health. For example, researchers can use our genome to find out if a person is at risk for certain diseases and suggest ways to prevent them. They can also develop personalized medicine, which means someone can get specific treatments based on their DNA! 💉
Moreover, genomic research is used in agriculture, helping scientists create plants that grow better or resist diseases! 🌱
Overall, this research opens up new possibilities for improving our lives.
Read Less
Genetic Variation and Polymorphisms
Genetic variation is what makes each person unique! 🌈
Every person has small differences in their DNA, called polymorphisms. These differences may change things like hair color, height, or even how we taste. For example, some people can taste bitterness better than others because of a specific polymorphism in a gene called “ TAS2R38.” 🌍 These variations are important as they contribute to the differences between individuals. Scientists study these variations to understand more about health and diseases, which can help improve treatments for everyone.
Every person has small differences in their DNA, called polymorphisms. These differences may change things like hair color, height, or even how we taste. For example, some people can taste bitterness better than others because of a specific polymorphism in a gene called “ TAS2R38.” 🌍 These variations are important as they contribute to the differences between individuals. Scientists study these variations to understand more about health and diseases, which can help improve treatments for everyone.
Read Less
Ethical Considerations in Genome Editing
Genome editing is an exciting but careful topic! ⚖
️ Scientists can change small parts of DNA using techniques like CRISPR. This can help fix genetic problems, but it raises important questions. For example, should we change an embryo’s DNA to prevent diseases? What if it changes a person in unexpected ways? 🤔
Scientists and ethicists want to ensure that these powerful tools are used safely and responsibly. They discuss the implications, like fairness and equality, to make sure everyone benefits from these discoveries without harm.
️ Scientists can change small parts of DNA using techniques like CRISPR. This can help fix genetic problems, but it raises important questions. For example, should we change an embryo’s DNA to prevent diseases? What if it changes a person in unexpected ways? 🤔
Scientists and ethicists want to ensure that these powerful tools are used safely and responsibly. They discuss the implications, like fairness and equality, to make sure everyone benefits from these discoveries without harm.
Read Less
Try your luck with the Human Genome Quiz.
Try this Human Genome quiz and see how many you score!
Q1
Question 1 of 10
Next
Explore More