Present
Facts for Kids
A genome is the complete set of genetic information that tells an organism how to grow and function, similar to a recipe book with instructions for life.

Explore the internet with AstroSafe
Search safely, manage screen time, and remove ads and inappropriate content with the AstroSafe Browser.
Download
Inside this Article
Bioinformatics
Messenger Rna
Human Genome
Information
Fruit Fly
Insurance
Medicine
Genomics
Protein
Health
Dna
Did you know?
🧬 A genome includes all the genes that make up an organism.
📚 Our genome is like a recipe book, guiding our growth and development.
🌟 Humans share 99.9% of their genome with other humans, with only 0.1% making us unique!
🌀 DNA, the building block of our genome, is shaped like a twisted ladder called a double helix.
🔍 Scientists completed the first human genome in 2003 as part of the Human Genome Project.
🌿 Different organisms have different genome sizes; for example, a fruit fly has around 165 million base pairs!
🌈 Genomic variation means no two genomes are the same, even among siblings.
💡 Gene expression is like a light switch, controlling which genes are active in our cells.
🍽️ During translation, proteins are made from instructions carried by mRNA.
🚀 Technological advancements in genomics help researchers unlock secrets about life on Earth.
Show Less

Become a Creator with DIY.org
A safe online space featuring over 5,000 challenges to create, explore and learn in.
Learn more
Overview
Have you ever wondered what makes you, YOU? 🤔
It’s something called a genome! A genome is basically the complete set of genetic instructions that tells our bodies how to grow, develop, and function. It’s like a recipe book full of information! 📚
All living things, including plants, animals, and humans, have genomes. Our genome is made up of DNA, which is found in almost every cell in our body. Just like a puzzle, all the pieces of our genome fit together to make us unique! 🌟
Scientists study genomes to learn more about life on Earth.
It’s something called a genome! A genome is basically the complete set of genetic instructions that tells our bodies how to grow, develop, and function. It’s like a recipe book full of information! 📚
All living things, including plants, animals, and humans, have genomes. Our genome is made up of DNA, which is found in almost every cell in our body. Just like a puzzle, all the pieces of our genome fit together to make us unique! 🌟
Scientists study genomes to learn more about life on Earth.
Read Less
Structure of DNA
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is shaped like a twisted ladder, known as a double helix! 🌀
This special shape makes it perfect for storing information. Each rung of the ladder is made from four chemicals called nucleotides, which are abbreviated as A, T, C, and G. Each one pairs up: A with T and C with G. Together, they create a code that tells our bodies what to do! 📊
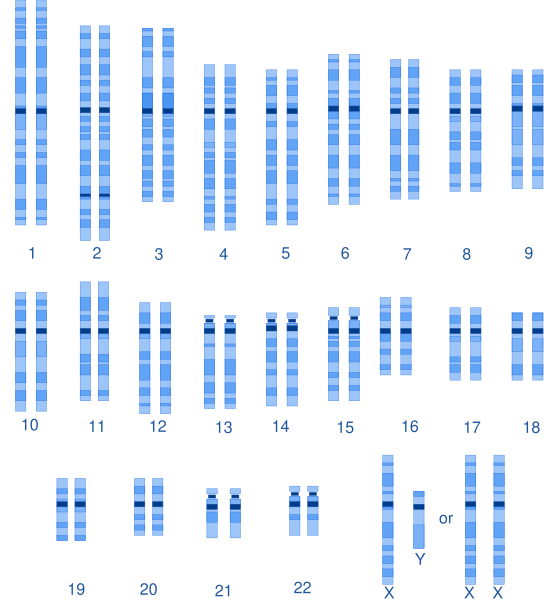
Every living thing has DNA in its cells, and it’s organized into chromosomes. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which are arranged in 23 pairs!
This special shape makes it perfect for storing information. Each rung of the ladder is made from four chemicals called nucleotides, which are abbreviated as A, T, C, and G. Each one pairs up: A with T and C with G. Together, they create a code that tells our bodies what to do! 📊
Every living thing has DNA in its cells, and it’s organized into chromosomes. Humans have 46 chromosomes, which are arranged in 23 pairs!
Read Less
Types of Genomes
Genomes can vary greatly among different organisms! 🌿
For example, a fruit fly has about 165 million base pairs in its genome, while a giant redwood tree has around 27 billion! 🌲
Humans lie somewhere in between with about 3 billion base pairs! Some organisms have small genomes, like bacteria, while others, like ferns, have huge genomes. These variations help scientists understand how different species adapt and survive in their environments! 📈
Also, plants and animals have their specific "complete sets" of genomes, which scientists can study to learn about evolution!
For example, a fruit fly has about 165 million base pairs in its genome, while a giant redwood tree has around 27 billion! 🌲
Humans lie somewhere in between with about 3 billion base pairs! Some organisms have small genomes, like bacteria, while others, like ferns, have huge genomes. These variations help scientists understand how different species adapt and survive in their environments! 📈
Also, plants and animals have their specific "complete sets" of genomes, which scientists can study to learn about evolution!
Read Less
Genomic Variation
No two genomes are exactly the same, even in the same species! This is called genomic variation. 🌈
For instance, siblings share 50% of their genes but can have different traits like hair color or height! Genomic variation arises from tiny changes in DNA called mutations. 🦠
Sometimes, these mutations don’t do much, but other times they can affect how a person looks or their health. This diversity is important because it helps populations adapt to changing environments. For example, some animals can survive in colder climates because of hereditary traits that result from genomic variation! ❄
️
For instance, siblings share 50% of their genes but can have different traits like hair color or height! Genomic variation arises from tiny changes in DNA called mutations. 🦠
Sometimes, these mutations don’t do much, but other times they can affect how a person looks or their health. This diversity is important because it helps populations adapt to changing environments. For example, some animals can survive in colder climates because of hereditary traits that result from genomic variation! ❄
️
Read Less
What is a Genome?
A genome includes all the genes in an organism! 🧬
Genes are tiny segments of DNA that carry instructions for making proteins, which do most of the work in our bodies. For humans, the entire genome has about 20,000 to 25,000 genes! 😲
Did you know our genomes are 99.9% the same as other humans? But it’s that tiny 0.1% that makes us different! The first complete human genome was sequenced in 2003, thanks to a big project called the Human Genome Project. 🌍
This exciting project helped scientists learn how our genes work and how they affect our health!
Genes are tiny segments of DNA that carry instructions for making proteins, which do most of the work in our bodies. For humans, the entire genome has about 20,000 to 25,000 genes! 😲
Did you know our genomes are 99.9% the same as other humans? But it’s that tiny 0.1% that makes us different! The first complete human genome was sequenced in 2003, thanks to a big project called the Human Genome Project. 🌍
This exciting project helped scientists learn how our genes work and how they affect our health!
Read Less
Genomics and Evolution
Genomics helps us understand how life has changed over time! 🕰
️ By studying the genomes of different species, scientists can trace their evolutionary history. For example, by comparing human DNA to that of chimpanzees, we’ve learned that we share about 98% of our genes! 🐒
This shows how closely related we are! Scientists use genomic tools to study fossils and ancient DNA, unlocking secrets about extinct species. 🦖
This understanding helps us see how living organisms adjust to their environments which is vital for their survival!
️ By studying the genomes of different species, scientists can trace their evolutionary history. For example, by comparing human DNA to that of chimpanzees, we’ve learned that we share about 98% of our genes! 🐒
This shows how closely related we are! Scientists use genomic tools to study fossils and ancient DNA, unlocking secrets about extinct species. 🦖
This understanding helps us see how living organisms adjust to their environments which is vital for their survival!
Read Less
Applications of Genomics
Genomics has many real-world uses! 🌍
In medicine, researchers use genomics to create personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s unique genes. This means doctors can prescribe the most effective drugs for each person! 🎯
Genomics also helps farmers create crops that resist diseases or grow better in certain climates, ensuring enough food for everyone! 🌽
Furthermore, environmentalists study the genomic diversity of species to help protect endangered animals. 🦏
The applications of genomics are helping improve health, agriculture, and nature’s conservation efforts!
In medicine, researchers use genomics to create personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s unique genes. This means doctors can prescribe the most effective drugs for each person! 🎯
Genomics also helps farmers create crops that resist diseases or grow better in certain climates, ensuring enough food for everyone! 🌽
Furthermore, environmentalists study the genomic diversity of species to help protect endangered animals. 🦏
The applications of genomics are helping improve health, agriculture, and nature’s conservation efforts!
Read Less
Transcription and Translation
Transcription and translation are two key steps in how our cells use genes! 🛠
️ First, during transcription, a gene's information from DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) inside the nucleus of the cell. Think of mRNA as a messenger carrying instructions! 📜
Then, during translation, this mRNA moves to a part of the cell called the ribosome, where proteins are made. The ribosome reads the mRNA and assembles the amino acids in the correct order to create a protein! 🍽
️ Proteins are essential for many functions in our bodies and help build everything from muscles to enzymes!
️ First, during transcription, a gene's information from DNA is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA) inside the nucleus of the cell. Think of mRNA as a messenger carrying instructions! 📜
Then, during translation, this mRNA moves to a part of the cell called the ribosome, where proteins are made. The ribosome reads the mRNA and assembles the amino acids in the correct order to create a protein! 🍽
️ Proteins are essential for many functions in our bodies and help build everything from muscles to enzymes!
Read Less
Gene Expression and Regulation
Gene expression is a process that decides which genes are "turned on" or "turned off" in our cells. 🔦
Not all genes are active at the same time, even though they are all present! This regulation helps our cells know what to do; for example, skin cells behave differently than muscle cells. Some genes are responsible for making hormones that help us grow! 📏
When a gene gets expressed, it produces a protein. Scientists study this to understand diseases better and improve health treatments. It’s like controlling a light switch in a room! 💡
Not all genes are active at the same time, even though they are all present! This regulation helps our cells know what to do; for example, skin cells behave differently than muscle cells. Some genes are responsible for making hormones that help us grow! 📏
When a gene gets expressed, it produces a protein. Scientists study this to understand diseases better and improve health treatments. It’s like controlling a light switch in a room! 💡
Read Less
Technologies in Genome Research
Researching genomes is super exciting thanks to technology! 💻
Scientists use tools like DNA sequencing machines, which can read the order of nucleotides in DNA. Each machine helps unravel the mystery of genes faster than ever before! 🔍
Additionally, bioinformatics uses computers to analyze large amounts of genetic data. This technology helps researchers find patterns in genes linked to diseases, like diabetes. 🩺
New advancements, such as CRISPR, allow scientists to edit genes very precisely. This can help fight genetic disorders or improve crops! With technology, the possibilities are endless! 🚀
Scientists use tools like DNA sequencing machines, which can read the order of nucleotides in DNA. Each machine helps unravel the mystery of genes faster than ever before! 🔍
Additionally, bioinformatics uses computers to analyze large amounts of genetic data. This technology helps researchers find patterns in genes linked to diseases, like diabetes. 🩺
New advancements, such as CRISPR, allow scientists to edit genes very precisely. This can help fight genetic disorders or improve crops! With technology, the possibilities are endless! 🚀
Read Less
Ethical Considerations in Genomics
As we explore genomes, it’s important to think about ethics! ⚖
️ This means considering what’s right and wrong. For example, gene editing can be powerful, but we must be careful about how it is used. Should scientists change genes that could affect future generations? 🤷
♂️ Also, people have a right to privacy regarding their genetic information. 👀
If someone knows their genome, can that affect their ability to get a job or insurance? These questions are important to ensure all research is done fairly and safely! Open discussions help us approach genomics responsibly!
️ This means considering what’s right and wrong. For example, gene editing can be powerful, but we must be careful about how it is used. Should scientists change genes that could affect future generations? 🤷
♂️ Also, people have a right to privacy regarding their genetic information. 👀
If someone knows their genome, can that affect their ability to get a job or insurance? These questions are important to ensure all research is done fairly and safely! Open discussions help us approach genomics responsibly!
Read Less
Try your luck with the Genome Quiz.
Try this Genome quiz and see how many you score!
Q1
Question 1 of 10
Next
Explore More