Present
Facts for Kids
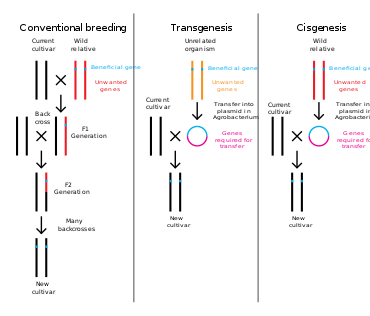
Genetic engineering is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology to help improve health, agriculture, and many other fields.

Explore the internet with AstroSafe
Search safely, manage screen time, and remove ads and inappropriate content with the AstroSafe Browser.
Download
Inside this Article
European Union
Stanley Cohen
Interference
Gene Therapy
Production
Population
Technology
Organism
Medicine
Society
Cloning
Did you know?
🩺 Gene therapy is a medical application of genetic engineering that helps fix faulty genes.
🌾 Genetic engineering increases food production by creating crops that resist pests and diseases.
🚜 Some genetically modified crops can withstand herbicides, making farming easier.
⚖️ Ethical discussions about genetic engineering help ensure that it's used responsibly.
🌱 Genetic engineering allows scientists to change an organism's genes to help it grow better.
🏥 This science has helped create important medicines, like insulin for people with diabetes.
🦠 The first major genetic engineering event happened in 1973 when scientists modified bacteria.
🍅 In 1994, the first genetically engineered food, a tomato, was created to last longer.
🔬 One method of genetic engineering is called 'gene cloning,' which makes copies of a specific gene.
✂️ CRISPR is a popular gene editing tool that makes precise changes to genes.
Show Less

Become a Creator with DIY.org
A safe online space featuring over 5,000 challenges to create, explore and learn in.
Learn more
Overview
Genetic engineering is a way scientists change an organism's genes, or the instructions that tell it how to grow and develop. 🌱
By using special tools and techniques, they can add, delete, or change these instructions. This science helps us with many things, like making plants stronger or creating medicines for diseases. 🏥
Imagine building with Legos; each piece is like a gene, and genetic engineering lets you change the design! Many plants, animals, and even tiny bacteria have been genetically engineered to help people in different ways. 🌍
Isn't that amazing?
By using special tools and techniques, they can add, delete, or change these instructions. This science helps us with many things, like making plants stronger or creating medicines for diseases. 🏥
Imagine building with Legos; each piece is like a gene, and genetic engineering lets you change the design! Many plants, animals, and even tiny bacteria have been genetically engineered to help people in different ways. 🌍
Isn't that amazing?
Read Less
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is an exciting use of genetic engineering in medicine! This technique replaces or fixes faulty genes in people, helping to treat or even cure genetic diseases. 🧬
For example, children with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also known as "bubble boy syndrome," can often be helped with gene therapy. 🤗
Scientists take healthy copies of the gene and put them into patients, helping their immune systems work better! Research in gene therapy continues to grow, and new treatments are being explored for conditions like cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy.
For example, children with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), also known as "bubble boy syndrome," can often be helped with gene therapy. 🤗
Scientists take healthy copies of the gene and put them into patients, helping their immune systems work better! Research in gene therapy continues to grow, and new treatments are being explored for conditions like cystic fibrosis and muscular dystrophy.
Read Less
CRISPR Technology
CRISPR is a revolutionary tool in genetic engineering! Created in 2012, it allows scientists to edit genes easily and accurately. 🧪
CRISPR works like a pair of guided scissors, cutting out or adding pieces of DNA to change how an organism functions. For example, scientists are exploring ways to use CRISPR to help crops grow better in droughts or pests. 🌻
This technology has made gene editing faster and cheaper, sparking new research and discoveries in many fields, including medicine and agriculture. 🚀
It’s a game-changer!
CRISPR works like a pair of guided scissors, cutting out or adding pieces of DNA to change how an organism functions. For example, scientists are exploring ways to use CRISPR to help crops grow better in droughts or pests. 🌻
This technology has made gene editing faster and cheaper, sparking new research and discoveries in many fields, including medicine and agriculture. 🚀
It’s a game-changer!
Read Less
Ethical Considerations
Like other powerful tools, genetic engineering comes with responsibilities! ⚖
️ Scientists and society discuss important questions, such as whether it's fair to change nature. Some people worry it might harm animals or plants. 🐒
Others are concerned about long-term effects that we might not see right away. Many scientists believe it’s important to think carefully and act responsibly. They follow guidelines to ensure safety and protect the environment! 🌳
Open conversation helps everyone understand the benefits and risks of genetic engineering.
️ Scientists and society discuss important questions, such as whether it's fair to change nature. Some people worry it might harm animals or plants. 🐒
Others are concerned about long-term effects that we might not see right away. Many scientists believe it’s important to think carefully and act responsibly. They follow guidelines to ensure safety and protect the environment! 🌳
Open conversation helps everyone understand the benefits and risks of genetic engineering.
Read Less
Regulations and Safety
Countries around the world have rules for genetic engineering! 🏛
️ These rules help keep people, animals, and the environment safe. For example, in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) checks new genetically engineered foods before they are sold. 🥦
In Europe, the European Union has strict rules that require labeling of genetically modified foods. 📜
These regulations help ensure that everyone knows what they are eating and that the food is safe! Following these rules helps scientists make smart choices.
️ These rules help keep people, animals, and the environment safe. For example, in the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) checks new genetically engineered foods before they are sold. 🥦
In Europe, the European Union has strict rules that require labeling of genetically modified foods. 📜
These regulations help ensure that everyone knows what they are eating and that the food is safe! Following these rules helps scientists make smart choices.
Read Less
Public Perception and Debate
Genetic engineering sparks lots of conversations! 🗣
️ Some people are excited about its potential, while others are worried about its safety and effects on the environment. 🌍
In schools, people learn both the benefits and risks. Many support research because it can create new medicines or better food. However, others wish to limit its use, believing nature should be preserved without human interference. It’s important to share ideas and ask questions! Engaging in open discussions helps everyone learn and decide what's best for our world. 💭
️ Some people are excited about its potential, while others are worried about its safety and effects on the environment. 🌍
In schools, people learn both the benefits and risks. Many support research because it can create new medicines or better food. However, others wish to limit its use, believing nature should be preserved without human interference. It’s important to share ideas and ask questions! Engaging in open discussions helps everyone learn and decide what's best for our world. 💭
Read Less
History of Genetic Engineering
The story of genetic engineering started a long time ago! The first major event was in 1973 when scientists Herbert Boyer and Stanley Cohen created a genetically modified bacteria that could make insulin, a medicine used by people with diabetes. 🦠
This was like opening a treasure chest of possibilities! Over the years, more discoveries followed. In 1994, scientists created the first genetically engineered food, a tomato that could last longer! 🍅
Since then, many plants and animals have been genetically engineered to help farmers and doctors.
This was like opening a treasure chest of possibilities! Over the years, more discoveries followed. In 1994, scientists created the first genetically engineered food, a tomato that could last longer! 🍅
Since then, many plants and animals have been genetically engineered to help farmers and doctors.
Read Less
Future Prospects and Innovations
The future of genetic engineering holds exciting possibilities! 🚀
Scientists are working on ways to create "designer" organisms that can solve problems, like cleaning up pollution or generating clean energy. 🌎
They may also develop treatments for currently untouchable diseases. Moreover, advancements in CRISPR and other techniques are happening quickly. 🌟
Future innovations could lead to better food production and even help endangered species survive. Collaboration between scientists, lawmakers, and the community is essential to ensure responsible advancements for everyone!
Scientists are working on ways to create "designer" organisms that can solve problems, like cleaning up pollution or generating clean energy. 🌎
They may also develop treatments for currently untouchable diseases. Moreover, advancements in CRISPR and other techniques are happening quickly. 🌟
Future innovations could lead to better food production and even help endangered species survive. Collaboration between scientists, lawmakers, and the community is essential to ensure responsible advancements for everyone!
Read Less
Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
Genetic engineering has made farming easier and more productive! 🌾
Scientists create crops that are resistant to pests and diseases, meaning farmers can use fewer chemicals! For example, “Roundup Ready” soybeans can tolerate certain herbicides, allowing farmers to control weeds better. 🚜
Some rice varieties have been genetically modified to grow in salty soils, helping farmers in tough climates. 🌊
These modifications help increase food supply, which is important as the world’s population grows! Farmers around the globe are using these advancements to feed more people.
Scientists create crops that are resistant to pests and diseases, meaning farmers can use fewer chemicals! For example, “Roundup Ready” soybeans can tolerate certain herbicides, allowing farmers to control weeds better. 🚜
Some rice varieties have been genetically modified to grow in salty soils, helping farmers in tough climates. 🌊
These modifications help increase food supply, which is important as the world’s population grows! Farmers around the globe are using these advancements to feed more people.
Read Less
Applications of Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering has many exciting applications! In medicine, it helps create new treatments for diseases, like gene therapy, where faulty genes are fixed to treat illnesses. 🩺
In agriculture, it increases food production and improves plants to resist pests or grow in tough climates. 🍏
For example, scientists developed “Bt cotton,” which is resistant to certain insects. Animals can also be genetically engineered for better growth or health. 🐄
Overall, genetic engineering is like using science to get bigger, stronger, healthier results!
In agriculture, it increases food production and improves plants to resist pests or grow in tough climates. 🍏
For example, scientists developed “Bt cotton,” which is resistant to certain insects. Animals can also be genetically engineered for better growth or health. 🐄
Overall, genetic engineering is like using science to get bigger, stronger, healthier results!
Read Less
Techniques Used in Genetic Engineering
Scientists use several cool techniques to change genes! One method is called "gene cloning," where they make copies of a specific gene to study or use it. 🔬
Another method is "gene editing," which is like using scissors to cut and paste genes. The most popular gene editing tool is CRISPR, a technology that makes very precise changes. ✂
️ Scientists use these methods to ensure the new genes work well and do what we want them to do. Learning how to do this carefully is very important!
Another method is "gene editing," which is like using scissors to cut and paste genes. The most popular gene editing tool is CRISPR, a technology that makes very precise changes. ✂
️ Scientists use these methods to ensure the new genes work well and do what we want them to do. Learning how to do this carefully is very important!
Read Less
Try your luck with the Genetic Engineering Quiz.
Try this Genetic Engineering quiz and see how many you score!
Q1
Question 1 of 10
Next
Explore More