Present
Facts for Kids
Blackbody radiation refers to the idealized emissions of thermal radiation from a perfect absorber at thermal equilibrium, which can be described by Planck's law and related laws of thermodynamics.

Explore the internet with AstroSafe
Search safely, manage screen time, and remove ads and inappropriate content with the AstroSafe Browser.
Download
Inside this Article
Infrared Radiation
Quantum Mechanics
Temperature
Max Planck
Technology
Discovery
Universe
Orange
Earth
Light
Did you know?
🌌 A blackbody is an idealized physical object that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation, regardless of frequency or angle of incidence.
🌡️ The temperature of a blackbody determines the spectrum of radiation it emits, following Planck's law.
💡 A perfect blackbody reflects no radiation; it is a perfect absorber and emitter of thermal radiation.
⚛️ Blackbody radiation is characterized by its continuous spectrum, which depends solely on the temperature of the body.
📈 As the temperature increases, a blackbody emits radiation at shorter wavelengths, shifting towards the visible spectrum.
🌈 The peak wavelength of radiation emitted by a blackbody is inversely proportional to its temperature, described by Wien's Displacement Law.
⚖️ The Stefan-Boltzmann Law states that the total energy radiated per unit surface area of a blackbody is proportional to the fourth power of its temperature.
🧪 Real materials can approximate blackbody behavior, and the concept is used to derive the laws of thermal radiation.
🔬 The concept of a blackbody is fundamental in thermodynamics and quantum mechanics, aiding in the understanding of energy emission.
🌍 Blackbody radiation has practical applications in fields like astronomy, climate science, and thermal imaging.
Show Less

Become a Creator with DIY.org
A safe online space featuring over 5,000 challenges to create, explore and learn in.
Learn more
Overview
Have you ever noticed that objects, like the sun ☀️ or a glowing stove, give off heat and light? This happens because of a special idea called blackbody radiation. A blackbody is an ideal object that absorbs all light and heat hitting it. Imagine a perfect sponge that soaks up everything! 🌌
Scientists use blackbody radiation to understand how hot things emit light and heat. The hotter an object gets, like a star 🌟 or a candle 🕯️, the more light it produces. Learning about blackbody radiation helps us understand everything from light bulbs to the stars!
Scientists use blackbody radiation to understand how hot things emit light and heat. The hotter an object gets, like a star 🌟 or a candle 🕯️, the more light it produces. Learning about blackbody radiation helps us understand everything from light bulbs to the stars!
Read Less
Planck's Law
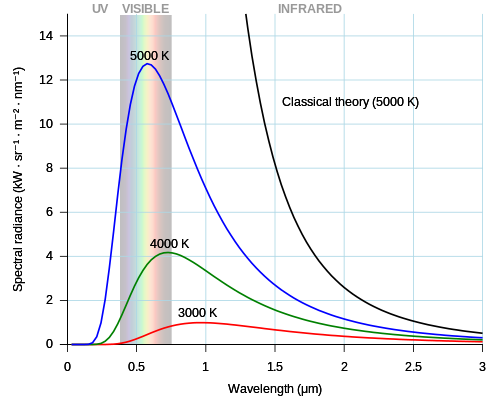
Planck's Law is a special equation that tells us how much light a blackbody gives off based on its temperature. 🌡
️ The formula involves the temperature (in Kelvin) and helps us find the intensity (brightness) of different wavelengths/colors of light. 🖍
️ For example, a blackbody at 5000 Kelvin, which is similar to our sun 🌞, shines the brightest at a wavelength of around 500 nanometers, which is blue-green light. This means that if we want to know how objects in space emit light, we can use Planck's Law!
️ The formula involves the temperature (in Kelvin) and helps us find the intensity (brightness) of different wavelengths/colors of light. 🖍
️ For example, a blackbody at 5000 Kelvin, which is similar to our sun 🌞, shines the brightest at a wavelength of around 500 nanometers, which is blue-green light. This means that if we want to know how objects in space emit light, we can use Planck's Law!
Read Less
Real-World Examples
Let’s look at some real-world examples of blackbody radiation! The sun ☀️ is a perfect example; it emits light and heat across space. When a metal gets very hot, it glows red, then orange, and finally bluish-white. 🔥
This is just like a blackbody! Another example is a hot stove 🔥 on the kitchen counter; it also emits blackbody radiation, producing heat and light. Lastly, thermal cameras pick up infrared radiation to help find warm objects, showing how blackbody radiation affects our daily lives! 🌍
This is just like a blackbody! Another example is a hot stove 🔥 on the kitchen counter; it also emits blackbody radiation, producing heat and light. Lastly, thermal cameras pick up infrared radiation to help find warm objects, showing how blackbody radiation affects our daily lives! 🌍
Read Less
Experimental Studies
Scientists conduct experiments to study blackbody radiation! 🔬
One famous experiment is the "cavities" experiment, where they heat up a blackbody cavity and measure the emitted light. They observe to see how different temperatures affect the colors of light emitted. A famous experiment is the "photoelectric effect," which helped confirm Planck's ideas. These experiments are important because they allow scientists to gather data and understand how energy works in so many different objects! 🧪
By conducting studies, we learn more about nature and the universe!
One famous experiment is the "cavities" experiment, where they heat up a blackbody cavity and measure the emitted light. They observe to see how different temperatures affect the colors of light emitted. A famous experiment is the "photoelectric effect," which helped confirm Planck's ideas. These experiments are important because they allow scientists to gather data and understand how energy works in so many different objects! 🧪
By conducting studies, we learn more about nature and the universe!
Read Less
Historical Background
The story of blackbody radiation begins in the late 19th century! 📅
In 1900, a German physicist named Max Planck introduced the idea of blackbody radiation. He discovered that hot objects release energy in little packets called quanta. 🎉
Planck's discovery changed how people understood energy and light! Before him, scientists thought energy was continuous, like a flowing river 🌊. But Planck showed us that it comes in small, separate pieces. In 1918, he even won the Nobel Prize for this important discovery! 🌟
His work laid the foundation for modern physics and quantum mechanics!
In 1900, a German physicist named Max Planck introduced the idea of blackbody radiation. He discovered that hot objects release energy in little packets called quanta. 🎉
Planck's discovery changed how people understood energy and light! Before him, scientists thought energy was continuous, like a flowing river 🌊. But Planck showed us that it comes in small, separate pieces. In 1918, he even won the Nobel Prize for this important discovery! 🌟
His work laid the foundation for modern physics and quantum mechanics!
Read Less
Theoretical Foundations
Max Planck discovered that the energy an object emits is related to its temperature. He created a formula that helps us calculate how much light and heat something releases at different temperatures. 📈
This formula is known as Planck's Law. It says that hotter objects produce more energy at shorter wavelengths, which means more blue and less red light! 🌡
️ So, a glowing star emits different colors depending on its temperature. If we understand this, we can learn about the universe better, including stars, planets, and other celestial objects. 🌌
This formula is known as Planck's Law. It says that hotter objects produce more energy at shorter wavelengths, which means more blue and less red light! 🌡
️ So, a glowing star emits different colors depending on its temperature. If we understand this, we can learn about the universe better, including stars, planets, and other celestial objects. 🌌
Read Less
Implications in Astrophysics
In astrophysics, blackbody radiation helps us understand stars! 🌌
Astronomers can use this idea to find out how hot and far away stars are. By measuring the light from distant stars, we can calculate their temperatures and compositions using blackbody radiation principles. Even our Earth 🌍 absorbs sunlight and radiates heat, which is essential for life. Understanding blackbody radiation helps us learn about not just our universe but also how planets and stars interact. So, blackbody radiation connects us to the cosmos! ✨
Astronomers can use this idea to find out how hot and far away stars are. By measuring the light from distant stars, we can calculate their temperatures and compositions using blackbody radiation principles. Even our Earth 🌍 absorbs sunlight and radiates heat, which is essential for life. Understanding blackbody radiation helps us learn about not just our universe but also how planets and stars interact. So, blackbody radiation connects us to the cosmos! ✨
Read Less
What is Blackbody Radiation?
Blackbody radiation is the way objects give off energy in the form of light 🌈 and heat. If something is a blackbody, it can take in energy without reflecting any, like a dark T-shirt on a sunny day! 🎽
Depending on how hot something is, it will glow different colors. A cool object may seem black or dark, but as it gets hotter, it might shine red, then orange, and even blue! 🔵
This color change happens because every color has its own energy. Blackbody radiation helps scientists learn about different temperatures in the universe!
Depending on how hot something is, it will glow different colors. A cool object may seem black or dark, but as it gets hotter, it might shine red, then orange, and even blue! 🔵
This color change happens because every color has its own energy. Blackbody radiation helps scientists learn about different temperatures in the universe!
Read Less
Applications of Blackbody Radiation
Blackbody radiation helps in many areas! 🔍
In technology, it helps us design better light bulbs 💡 and solar panels that capture sunlight. Scientists also use it to study stars. For example, astronomers can measure the light from stars to find their temperature and size using blackbody radiation principles. 🌠
In medicine, blackbody radiation helps in medical devices, such as thermal cameras that can see heat. Thus, understanding how blackbodies work can improve our everyday lives and technology! 💻
In technology, it helps us design better light bulbs 💡 and solar panels that capture sunlight. Scientists also use it to study stars. For example, astronomers can measure the light from stars to find their temperature and size using blackbody radiation principles. 🌠
In medicine, blackbody radiation helps in medical devices, such as thermal cameras that can see heat. Thus, understanding how blackbodies work can improve our everyday lives and technology! 💻
Read Less
Blackbody Radiation and Quantum Mechanics
Blackbody radiation helped create the exciting world of quantum mechanics! 🌀
Quantum mechanics studies how tiny particles, like atoms 🌌, behave. Before Max Planck's discovery, many thought energy was continuous. However, he showed that energy comes in tiny packets called quanta, which helped develop quantum theory. Scientists later found that the behavior of particles at small scales is very different from larger objects. As a result, quantum mechanics can explain things like how lasers work and how atoms bond, making it a crucial part of modern physics! 💫
Quantum mechanics studies how tiny particles, like atoms 🌌, behave. Before Max Planck's discovery, many thought energy was continuous. However, he showed that energy comes in tiny packets called quanta, which helped develop quantum theory. Scientists later found that the behavior of particles at small scales is very different from larger objects. As a result, quantum mechanics can explain things like how lasers work and how atoms bond, making it a crucial part of modern physics! 💫
Read Less
Try your luck with the Blackbody Radiation Quiz.
Try this Blackbody Radiation quiz and see how many you score!
Q1
Question 1 of 10
Next
Explore More