Present
Facts for Kids
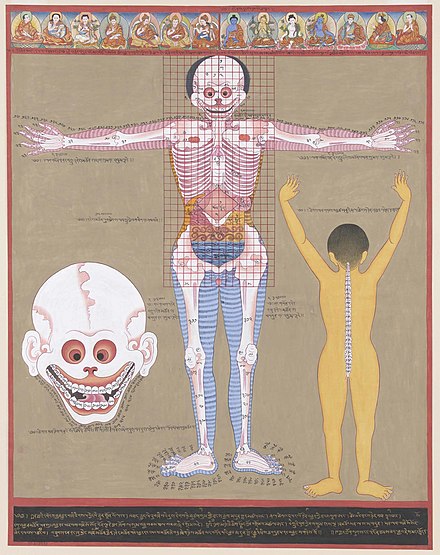
Anatomy is the study of the internal structure of organisms, helping us understand how living things function and grow.

Explore the internet with AstroSafe
Search safely, manage screen time, and remove ads and inappropriate content with the AstroSafe Browser.
Download
Inside this Article
Connective Tissue
Hippocrates
Detective
Breathing
Swimming
Becoming
Function
Medicine
Surgery
Future
Cold
Did you know?
🧠 Anatomy is the study of the inside of living things.
🔬 Cells are the tiny building blocks that make up all living things.
🤝 Tissues are groups of cells that work together to perform a special function.
💕 The human body has about 206 bones that provide movement and protection.
🐒 Human anatomy is different from animal anatomy, showcasing unique features.
✋ Red blood cells carry oxygen, while nerve cells help us think and feel.
🦓 Comparative anatomy teaches us about the similarities and differences among species.
🏋️ Functional anatomy examines how body parts work together for different functions.
🌱 Developmental anatomy looks at how organisms grow and change.
🩻 Imaging techniques help doctors see inside our bodies without surgery.
Show Less

Become a Creator with DIY.org
A safe online space featuring over 5,000 challenges to create, explore and learn in.
Learn more
Overview
Anatomy is the study of the inside of living things! 🧠
It helps us understand how animals and humans work. You can find anatomy everywhere—in plants, animals, and our bodies! For example, did you know that the human body has about 206 bones? This is important for movement and protection. In ancient times, people like Hippocrates and Galen studied anatomy to learn about health. Today, scientists and doctors still study anatomy to help us stay healthy! 🏥
Learning about anatomy can be super fun and helps us appreciate all living things around us. 🌍
It helps us understand how animals and humans work. You can find anatomy everywhere—in plants, animals, and our bodies! For example, did you know that the human body has about 206 bones? This is important for movement and protection. In ancient times, people like Hippocrates and Galen studied anatomy to learn about health. Today, scientists and doctors still study anatomy to help us stay healthy! 🏥
Learning about anatomy can be super fun and helps us appreciate all living things around us. 🌍
Read Less
Functional Anatomy
Functional anatomy looks at how body parts work together for certain functions! 🤔
For example, our heart pumps blood, and our lungs take in air. Each part of our bodies is designed to do a specific job. 🏃
♂️ Muscles contract to move bones, while nerves send messages from the brain to the body. Birds have light bones for flying, and cheetahs have strong muscles to run fast. By studying functional anatomy, we learn how each body part contributes to our survival and activities. It’s like being a detective, figuring out how everything fits! 🕵
️♂️
For example, our heart pumps blood, and our lungs take in air. Each part of our bodies is designed to do a specific job. 🏃
♂️ Muscles contract to move bones, while nerves send messages from the brain to the body. Birds have light bones for flying, and cheetahs have strong muscles to run fast. By studying functional anatomy, we learn how each body part contributes to our survival and activities. It’s like being a detective, figuring out how everything fits! 🕵
️♂️
Read Less
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy is a branch that looks at similarities and differences in the body structures of different species. 🦓
For instance, the arm of a human, the wing of a bird, and the flipper of a whale all have similar bones! They are called homologous structures and show how different animals can evolve from a common ancestor. 🔍
This helps scientists learn about evolution and how species adapt over time. By studying various animals, we can understand how bodies are built for different tasks, like running, flying, or swimming. It’s like finding clues in nature’s puzzle! 🧩
For instance, the arm of a human, the wing of a bird, and the flipper of a whale all have similar bones! They are called homologous structures and show how different animals can evolve from a common ancestor. 🔍
This helps scientists learn about evolution and how species adapt over time. By studying various animals, we can understand how bodies are built for different tasks, like running, flying, or swimming. It’s like finding clues in nature’s puzzle! 🧩
Read Less
Pathological Anatomy
Pathological anatomy is the study of diseases and how they affect body structures. 🦠
When we get sick, our cells and tissues can change. For example, when someone has a cold, their throat can swell up. Doctors use pathological anatomy to find out what’s wrong when we don’t feel well. 🔍
They study tissues and organs through biopsies and other tests. Understanding these changes helps doctors create better treatments to help us heal faster. Learning about diseases is important because it helps keep us healthy in the first place! ❤
️
When we get sick, our cells and tissues can change. For example, when someone has a cold, their throat can swell up. Doctors use pathological anatomy to find out what’s wrong when we don’t feel well. 🔍
They study tissues and organs through biopsies and other tests. Understanding these changes helps doctors create better treatments to help us heal faster. Learning about diseases is important because it helps keep us healthy in the first place! ❤
️
Read Less
Developmental Anatomy
Developmental anatomy studies how organisms grow and change from tiny cells into fully formed beings! 🌱
It starts with a fertilized egg, which begins to divide and grow into a baby. In humans, this process takes about nine months before the baby is born. 👶
Animals also go through developmental changes, like tadpoles becoming frogs. Scientists study these changes to learn about growth and development in different species. Knowing how our bodies develop can help doctors better understand health and treat illnesses. 🌍
It starts with a fertilized egg, which begins to divide and grow into a baby. In humans, this process takes about nine months before the baby is born. 👶
Animals also go through developmental changes, like tadpoles becoming frogs. Scientists study these changes to learn about growth and development in different species. Knowing how our bodies develop can help doctors better understand health and treat illnesses. 🌍
Read Less
Anatomical Terminology
Anatomical terminology is a special language that helps people describe the location of body parts! 🗣
️ For instance, "anterior" means the front, while "posterior" means the back. Doctors and scientists use these terms to communicate clearly. 🌌
Other important words include “superior” for above and “inferior” for below. By learning this language, we can understand how our bodies are organized and how to tell someone about a problem. It’s like having a secret code! Just imagine how much easier it makes working together in science and medicine! 🔑
️ For instance, "anterior" means the front, while "posterior" means the back. Doctors and scientists use these terms to communicate clearly. 🌌
Other important words include “superior” for above and “inferior” for below. By learning this language, we can understand how our bodies are organized and how to tell someone about a problem. It’s like having a secret code! Just imagine how much easier it makes working together in science and medicine! 🔑
Read Less
Tissues and Organ Systems
Tissues are groups of cells that work together. 🤝
There are four main types of tissues: muscle, connective, epithelial, and nervous. Muscle tissue helps us move, while connective tissue supports and connects parts of our body. Organs are made of different types of tissues working together. For example, the heart pumps blood, and the lungs help us breathe. 🫁
Organ systems are groups of organs that work together. The digestive system helps us break down food, while the nervous system helps us communicate and respond to our environment. It’s like a team of superheroes working together! 💪
There are four main types of tissues: muscle, connective, epithelial, and nervous. Muscle tissue helps us move, while connective tissue supports and connects parts of our body. Organs are made of different types of tissues working together. For example, the heart pumps blood, and the lungs help us breathe. 🫁
Organ systems are groups of organs that work together. The digestive system helps us break down food, while the nervous system helps us communicate and respond to our environment. It’s like a team of superheroes working together! 💪
Read Less
Cell Structure and Function
Cells are tiny building blocks that make up all living things! 🧬
Just like you need bricks to build a house, cells help us build our body. There are different types of cells, such as skin cells, muscle cells, and brain cells. Each type has a special job to do. For instance, red blood cells carry oxygen, while nerve cells help us think and feel. Cells work together to create tissues, like muscle or skin, that help our bodies function properly. Without cells, we wouldn’t be able to grow, run, or even think! 🚀
Just like you need bricks to build a house, cells help us build our body. There are different types of cells, such as skin cells, muscle cells, and brain cells. Each type has a special job to do. For instance, red blood cells carry oxygen, while nerve cells help us think and feel. Cells work together to create tissues, like muscle or skin, that help our bodies function properly. Without cells, we wouldn’t be able to grow, run, or even think! 🚀
Read Less
Imaging Techniques in Anatomy
Imaging techniques are tools that help us look inside our bodies without surgery! 🩻
Doctors use these technologies to see organs and tissues. Common imaging techniques include X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasounds. X-rays can help doctors see broken bones, while MRIs show soft tissues like muscles and organs. 🎮
Ultrasounds use sound waves to create images, often used for pregnant women to see their babies. These tools help scientists and doctors understand how our bodies look and work, making diagnosis easier and keeping us healthy! 📸
Doctors use these technologies to see organs and tissues. Common imaging techniques include X-rays, MRI scans, and ultrasounds. X-rays can help doctors see broken bones, while MRIs show soft tissues like muscles and organs. 🎮
Ultrasounds use sound waves to create images, often used for pregnant women to see their babies. These tools help scientists and doctors understand how our bodies look and work, making diagnosis easier and keeping us healthy! 📸
Read Less
Anatomy in Medicine and Research
Anatomy plays a significant role in medicine and research! 🩺
Doctors study anatomy to diagnose and treat illnesses. Surgeons need to know exactly where to cut to help patients. Research scientists study anatomy to develop new medicines and treatments. 🧪
They examine how diseases affect the body and how we can heal it. Learning anatomy helps us build healthier communities and improve our medical practices. The more we understand our bodies, the better we can take care of ourselves and each other! Together, we can work towards a healthier future! 🌈
Doctors study anatomy to diagnose and treat illnesses. Surgeons need to know exactly where to cut to help patients. Research scientists study anatomy to develop new medicines and treatments. 🧪
They examine how diseases affect the body and how we can heal it. Learning anatomy helps us build healthier communities and improve our medical practices. The more we understand our bodies, the better we can take care of ourselves and each other! Together, we can work towards a healthier future! 🌈
Read Less
Human Anatomy vs. Animal Anatomy
Human anatomy is different from animal anatomy, but both are fascinating! 🐒
For example, humans have an opposable thumb, allowing us to hold tools, while monkeys use their hands to swing through trees. 🐾
Animals have unique features, like fish gills for breathing underwater and bird wings for flying. Each species has adaptations that help them survive in their environment. Humans usually walk on two legs, while most animals walk on four. Learning about these differences helps us understand how all living things are special and adapted to their homes! 🌳
For example, humans have an opposable thumb, allowing us to hold tools, while monkeys use their hands to swing through trees. 🐾
Animals have unique features, like fish gills for breathing underwater and bird wings for flying. Each species has adaptations that help them survive in their environment. Humans usually walk on two legs, while most animals walk on four. Learning about these differences helps us understand how all living things are special and adapted to their homes! 🌳
Read Less
Try your luck with the Anatomy Quiz.
Try this Anatomy quiz and see how many you score!
Q1
Question 1 of 10
Next
Explore More